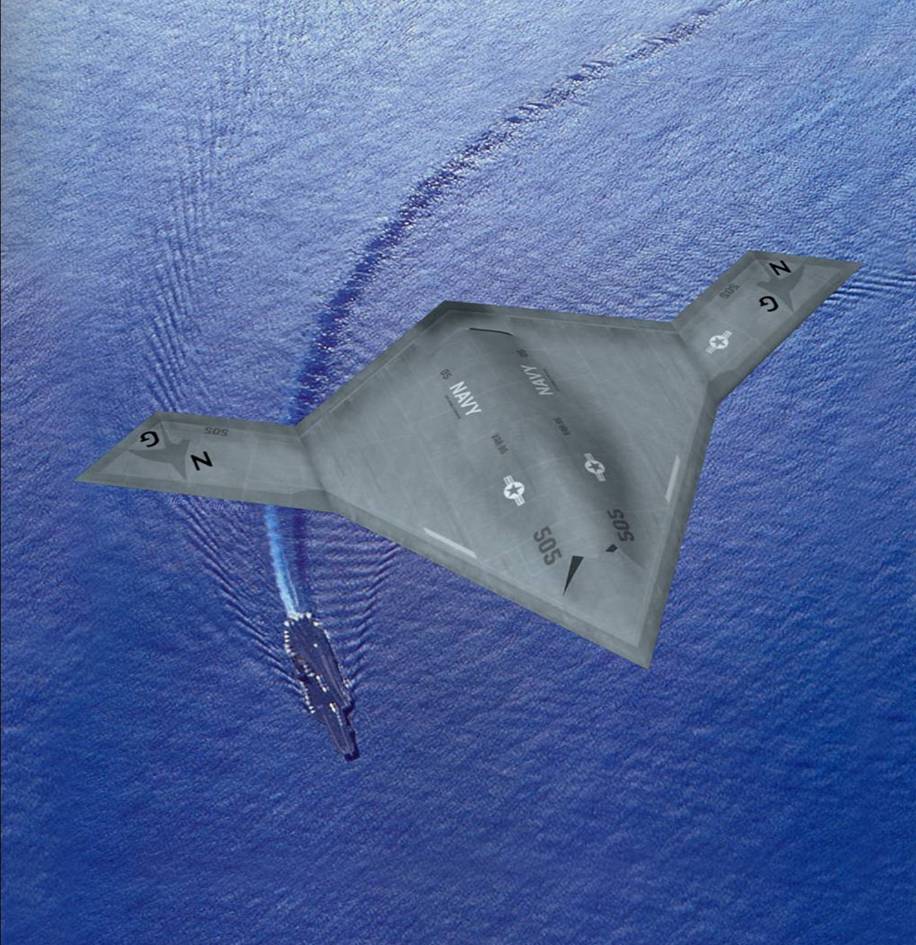
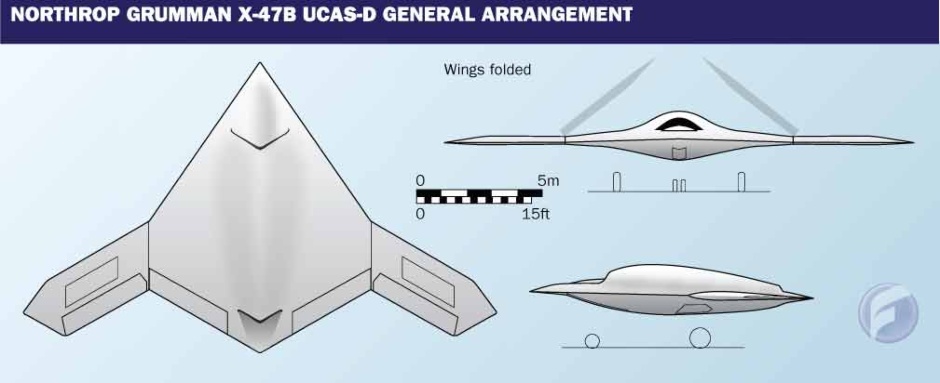
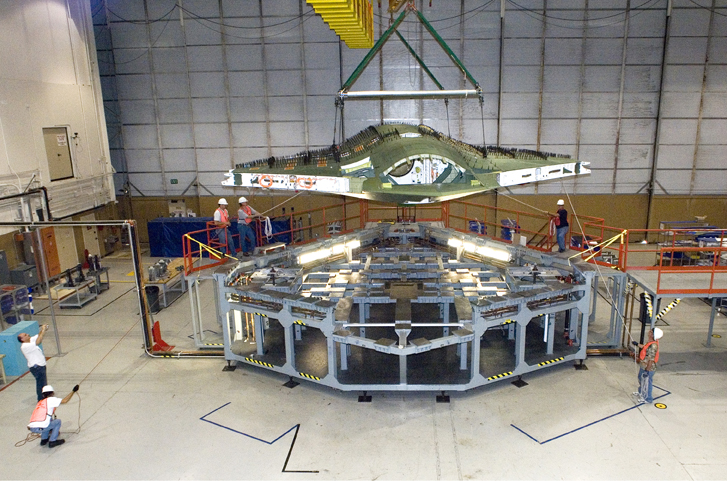
무인 스텔스 레이저 공격기 X-47B
[중앙일보] 2008년 05월 26일(월) 오전 02:11
군사전문가들은 현존 최고의 전투기인 F-22 는 인간이 조종하는 마지막 전투기가 될 것이라고 예고한다. 인간이 감당할 수 있는 중력의 한계가 9G(중력의 9배)이기 때문에 9G 이상의 기능을 요구하는 전투기는 무인항공기로 대체될 수밖에 없기 때문이다. 즉 인간의 몸으로는 급속하게 발전하는 비행기술을 감당할 수 없는 것이다.
또 유인기는 조종사의 안전을 위해 중량이 클 수밖에 없지만 무인기는 중량으로 부터 자유롭다. 플랫폼의 소형화로 속도와 기동성의 이점 있다. 경제성도 있다. 조종사의 양성비용과 운영비 등을 감안하면 무인기는 개발비와 운영비가 유인기의 절반 수준이다. 무인기의 가장 큰 잇점은 조종사의 안전을 고려하지 않아도 되기 때문에 기상조건에 구애받지 않으며 낮밤 가리지 않고 전천후 운영이 가능하다. 군사강국들이 무인기에 집착하는 이유가 바로 이 때문이다.
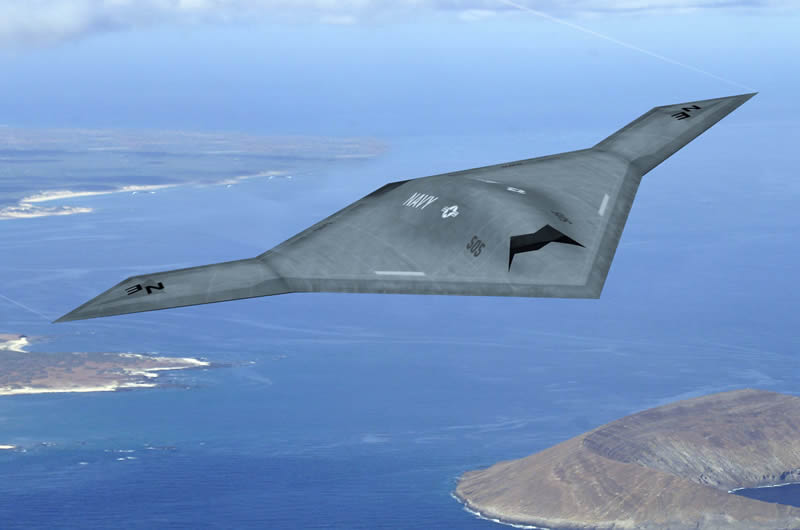
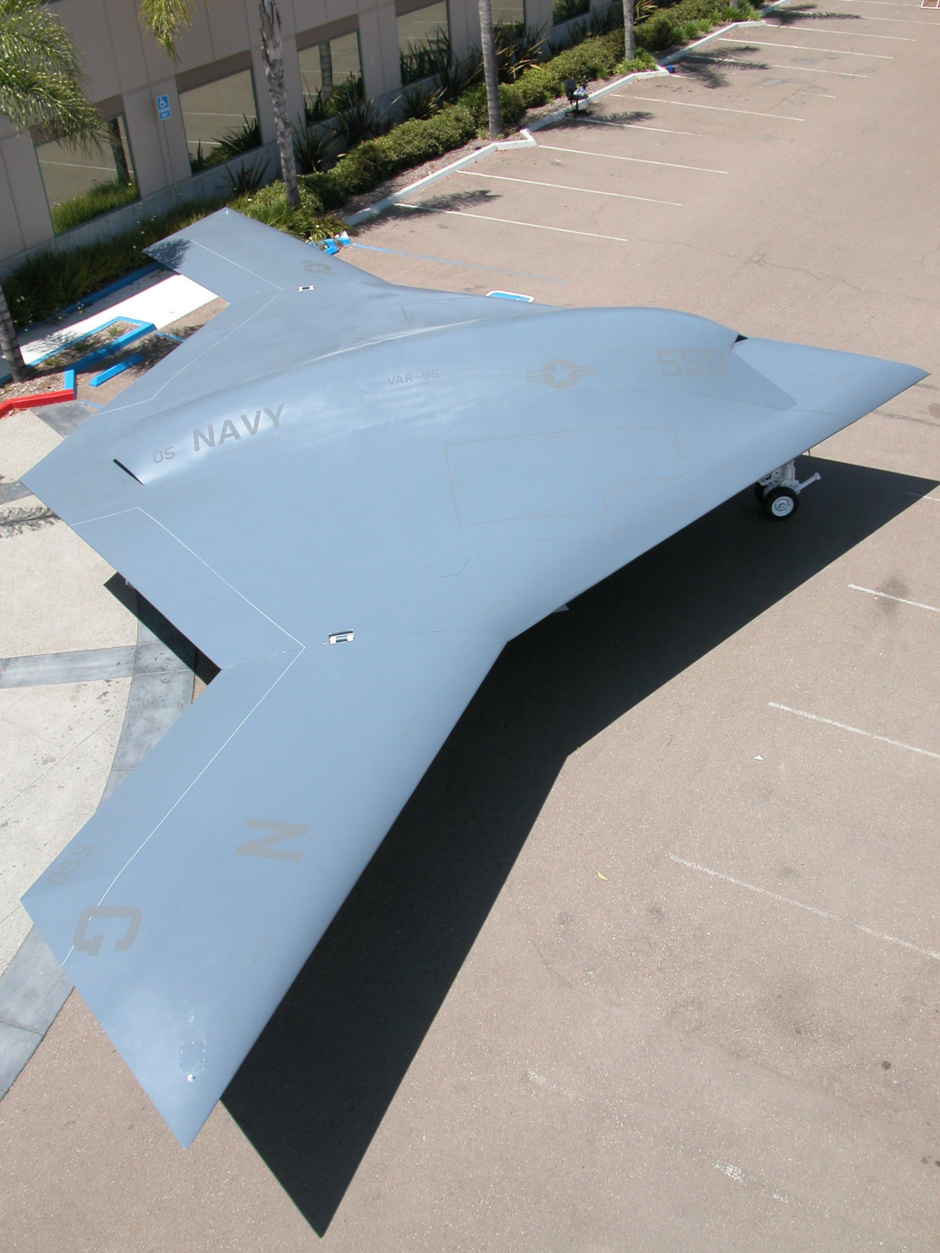
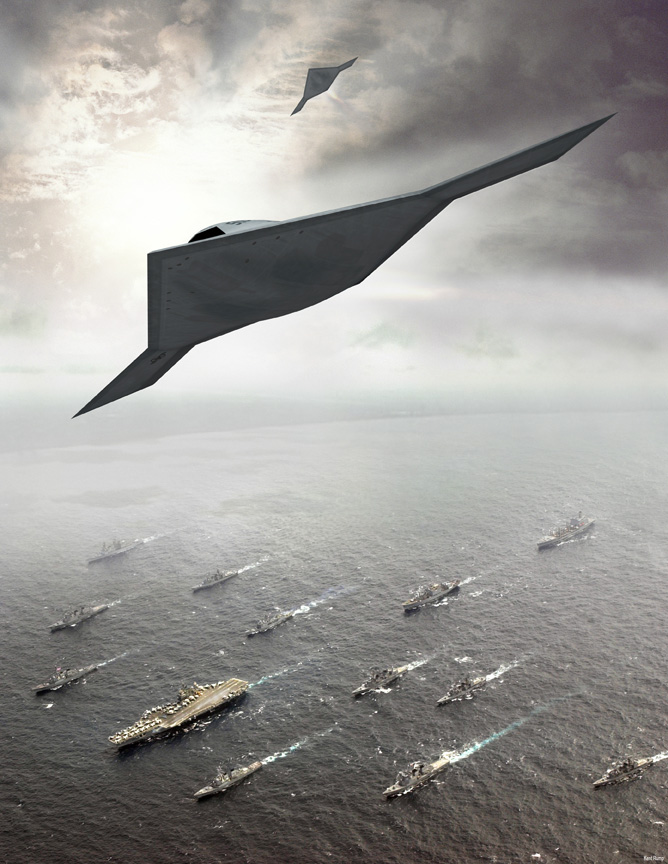
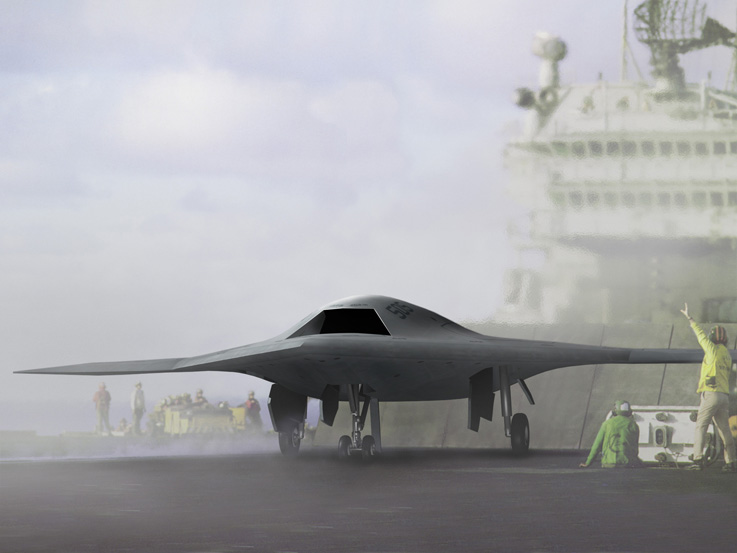
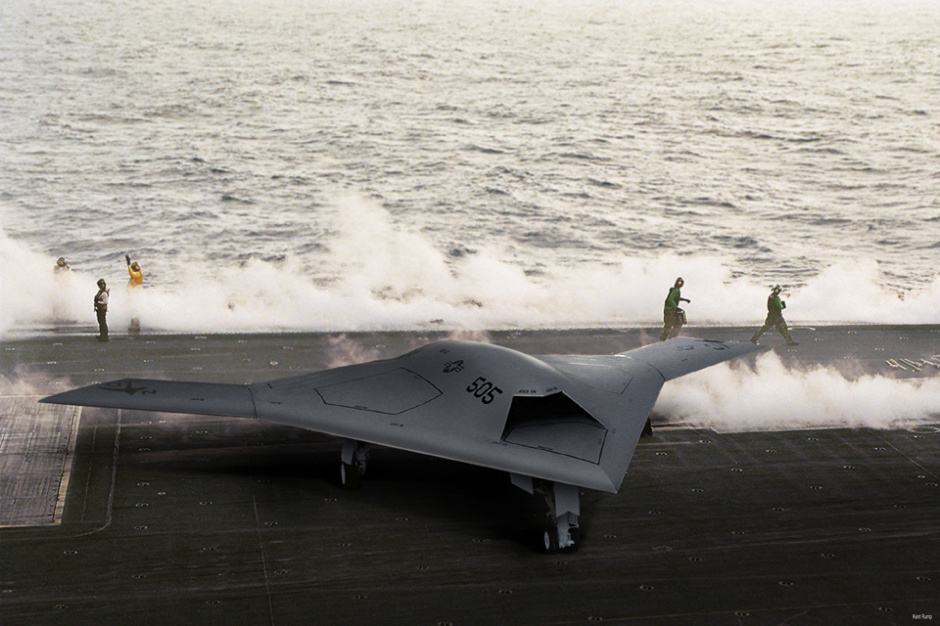
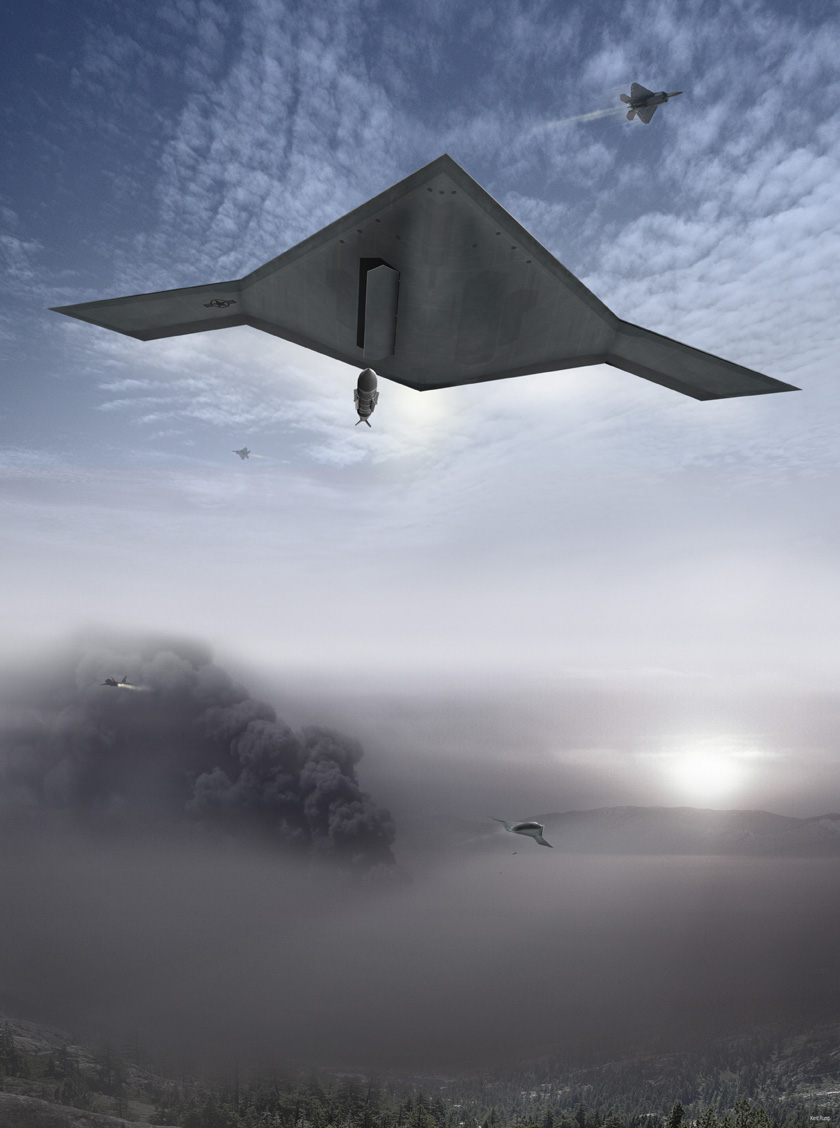
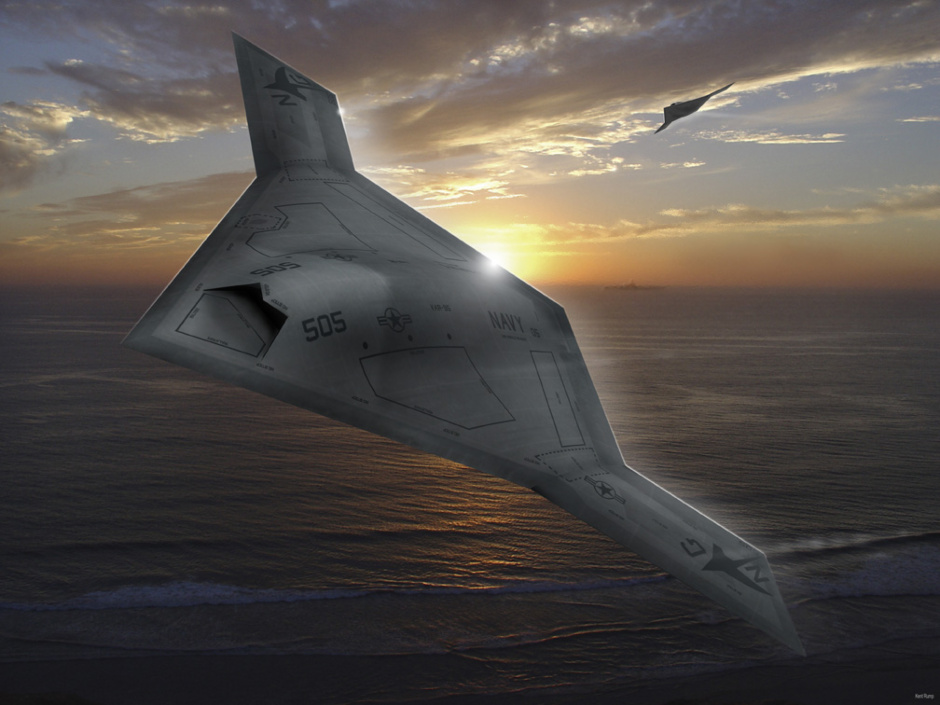
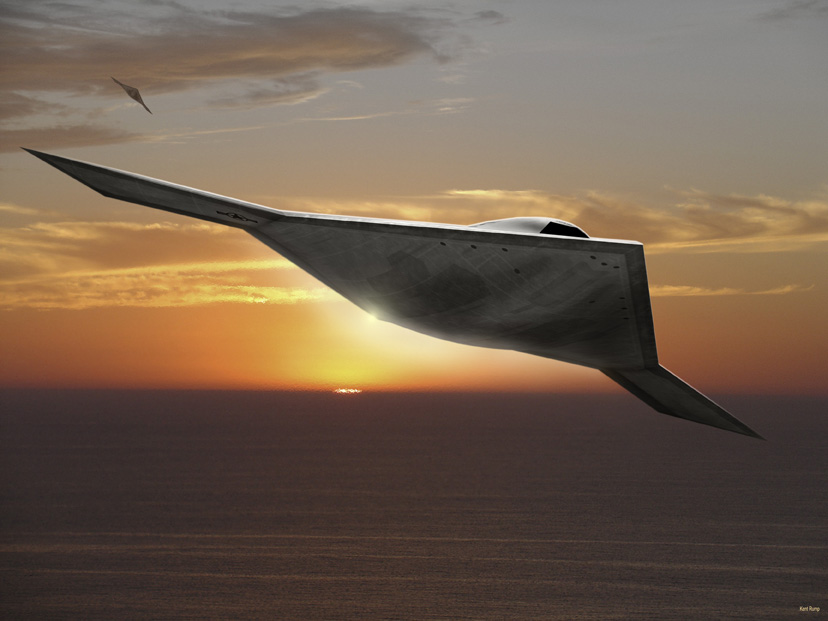
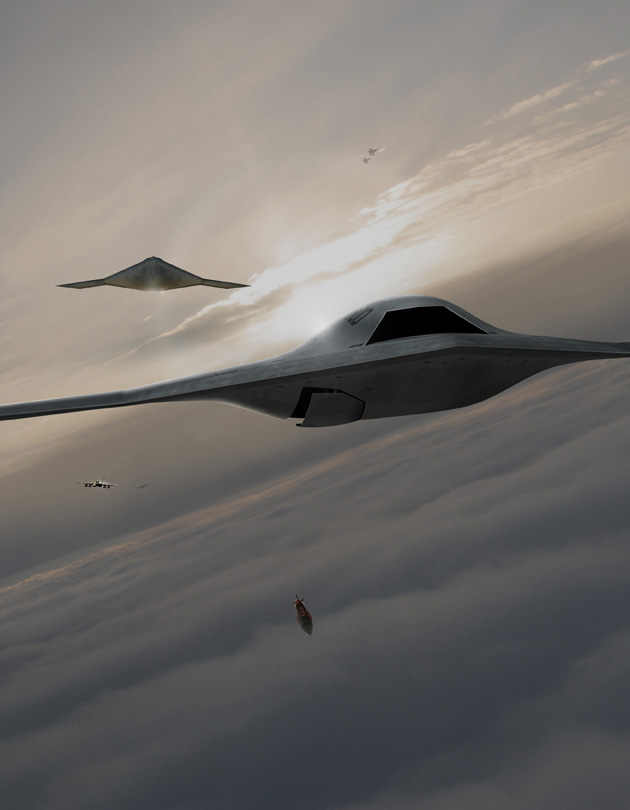
미국의 노드롭 그루만사는 2007년 8월 1일 미 해군과 개발비 6억3500만 달러의 개발비가 드는 무인공격기 시스템 (UCAS· Unmanned Combat Air Systems program)개발 협약을 맺었다. X-47B(사진)로 명명된 이 무인공격기는 미사일은 물론 레이저 무기 시스템을 장착한 것으로 현재 2대가 제작 중에 있다.
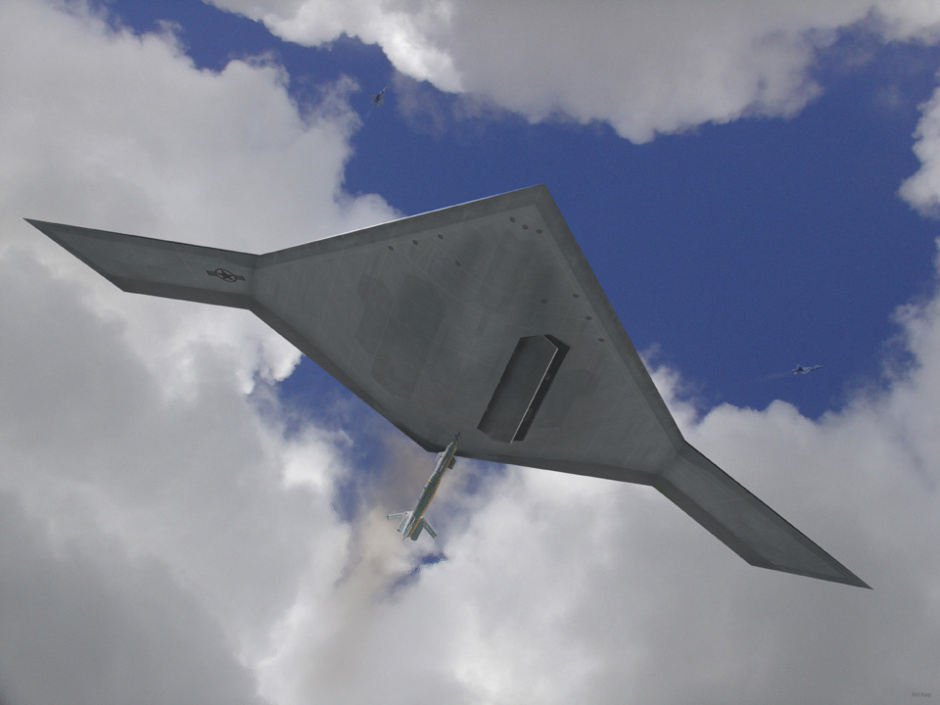
X-47B는 본격적인 무인공격기 시대를 열어나가 신호탄이다. 이스라엘의 무인폭격기 하피 등 소형 UAV나 미국의 정찰 공격기 프리데터가 개발돼 실전 배치됐지만 무기탑재량을 비롯해 그 기능은 매우 제한적이다. 반면 X-47B는 다목적 공격기다. 탑재되는 무기에서도 기존의 무인공격기와 비교가 안된다. X-47B는 레이저 광선과 고출력 마이크로파(HPM)로 적의 미사일과 통신시설을 파괴하는 가공할 공격력을 갖추고 있다. 레이저 무기 뿐 아니라 공대공, 공대지 미사일(최대2045kg)을 장착해 다양한 방법으로 적을 공격한다. 정찰기로서 기능도 수행한다. 초음속인데다 차세대 스텔스 기술을 채용해 적의 레이다에 잘 잡히지 않는다. 공중급유가 가능해 나흘간 연속작전을 벌일 수 있다. 항공모함에서 이착륙이 가능할 정도로 기동력도 있다. 작전반경이 2400km에 달한다. 가장 중요한 것은 조종사의 안전을 고려할 필요가 없는 무인공격기(UAV·Un-manned aerial vehicle)라는 점이다. 이정도면 '꿈의 전투기'라 불릴만 하다.
노드롭 그루만사 홈페이지(http://www.is.northropgrumman.com)에 따르면 X-47B는 2009년 말 시험비행에 들어가 2011년 항공모함 이착륙 훈련을 거쳐 2013년 개발 완료를 목표로 하고 있다. 미 해군 계획에 의하면 X-47B는 2020년 쯤 실전에 배치된다.
한편 보잉사는 이에 앞서 지난 2004년 무인전투기 X-45A(사진)가 캘리포니아 에드워드 공군기지를 이륙한 뒤 1만 m 상공에서 폭탄을 투하해 목표물인 트럭을 정확하게 명중시켰다고 발표한 바 있다. 실험에 이용된 X-45A는 사전에 목표물의 좌표가 입력됐고, GPS(위성위치확인시스템)를 이용해 항로를 조절했다. 미국의 3대 항공방산업체인 보잉, 노드롭 그루만, 록히드 마틴 사는 치열한 무인전투기 개발 경쟁을 벌이고 있다.
주기중 기자 ·동영상·사진=노드롭그루만, 보잉사 홈페이지
[중앙일보 주기중]
*************************************
X-47 Pegasus
Northrop Grumman X-47B
Type Unmanned Combat Aerial Vehicle
Manufacturer Northrop Grumman
Maiden flight February 2003
Primary user United States Navy
Produced 2003 - January 13, 2006
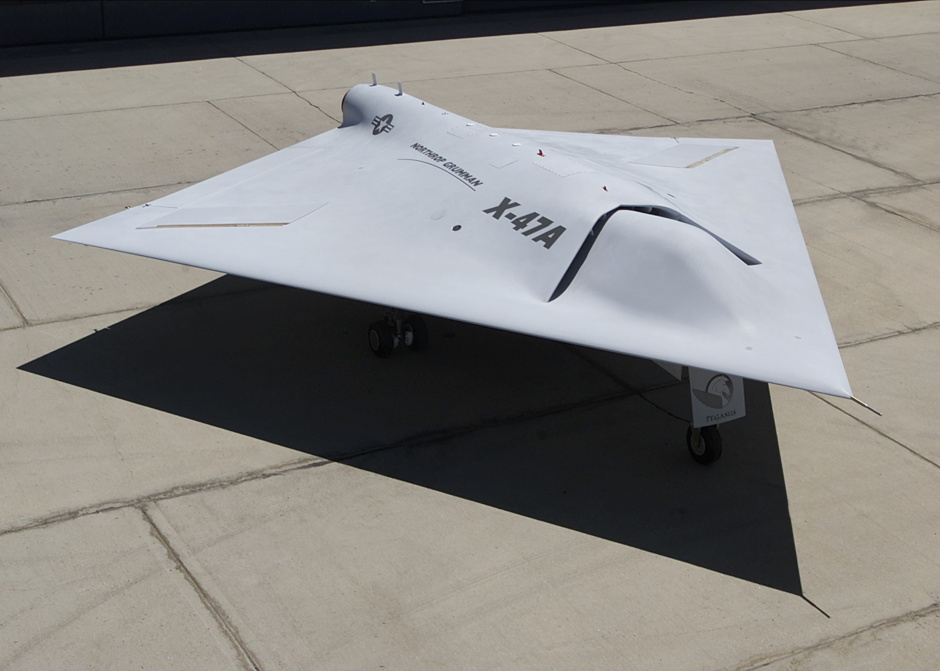
X-47A roll out
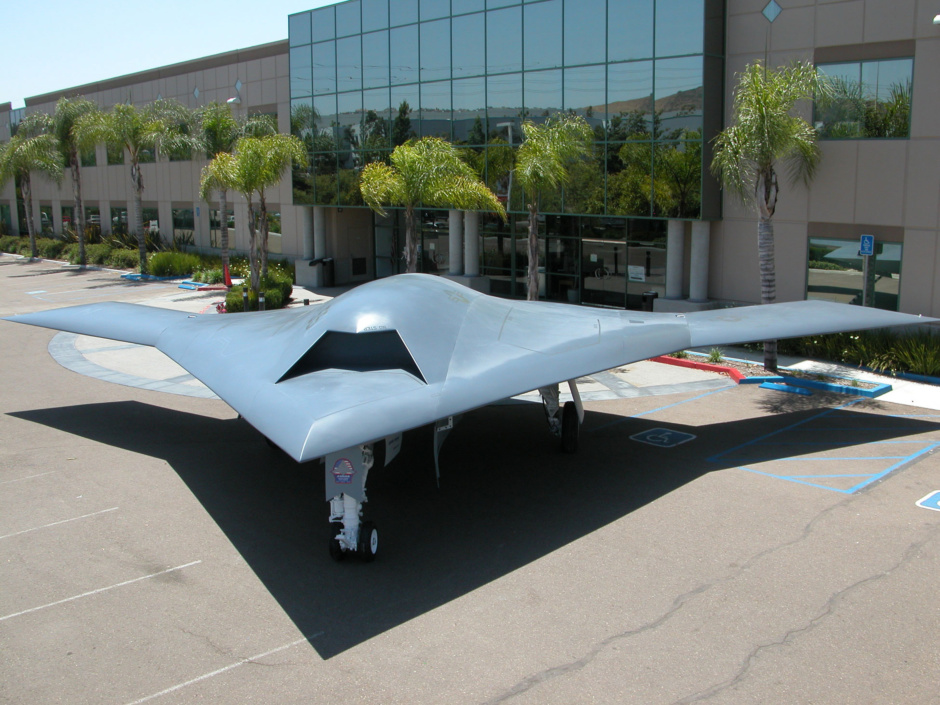
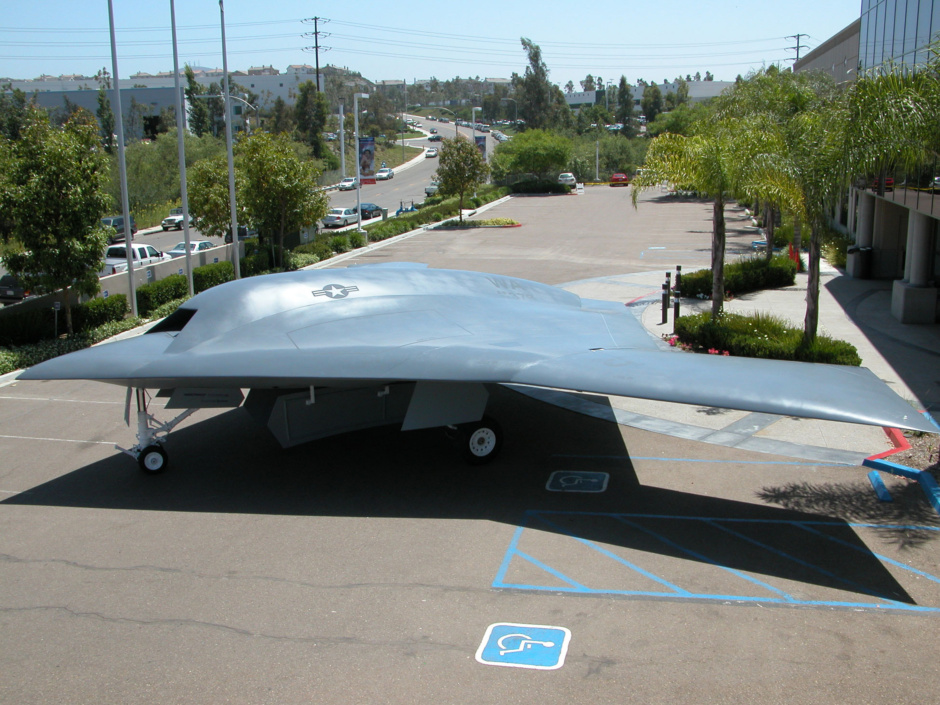
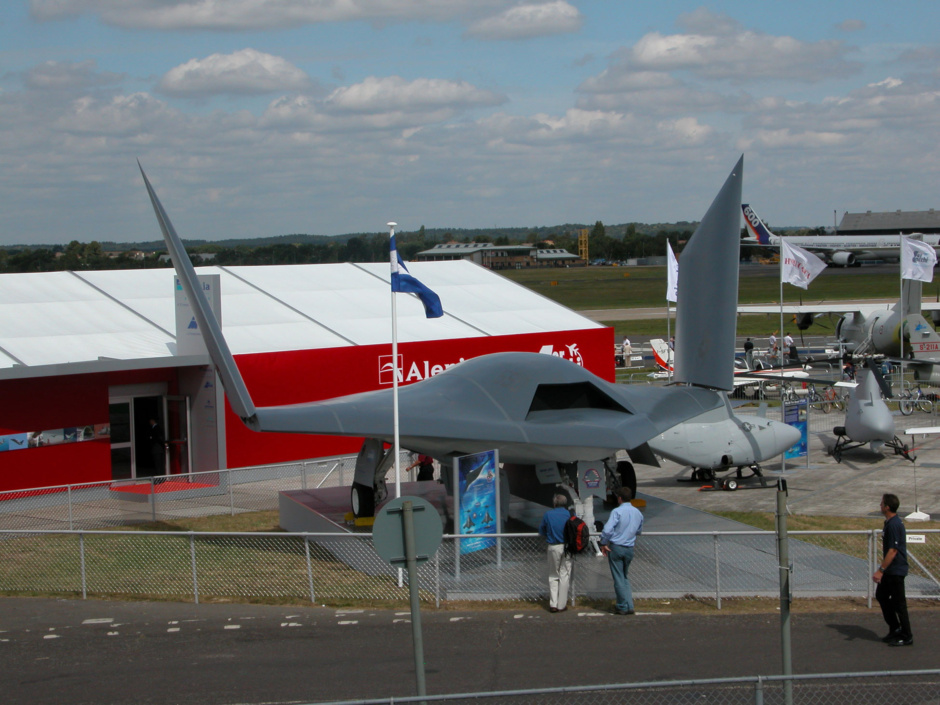
The Northrop Grumman X-47 Pegasus is a demonstration Unmanned Combat Aerial Vehicle. The X-47 began as part of DARPA's J-UCAS project, and is now part of the United States Navy's UCAS-D program to create a carrier-based unmanned aircraft.
Unlike the Boeing X-45, Pegasus development was company-funded. The initial vehicle carries the designation X-47A; the follow-on naval version is designated X-47B.
The proof-of-concept X-47A vehicle was built under contract by Burt Rutan's Scaled Composites at the Mojave Spaceport. The roll out ceremony at Mojave was in July 2001 and the first flight was successfully completed in February 2003. The program was terminated on January 13, 2006 as part of the US Military's Quadrennial Defense Review.
History
The US Navy did not commit to practical UCAV efforts until the summer of 2000, when the service awarded contracts of $2 million USD each to Boeing and Northrop Grumman for a 15-month concept-exploration program.
Design considerations for a naval UCAV included dealing with the corrosive salt-water environment, deck handling for launch and recovery, integration with command and control systems, and operation in a carrier's high electromagnetic interference environment. The Navy was also interested in using their UCAVs for reconnaissance missions, penetrating protected airspace to identify targets for the attack waves.
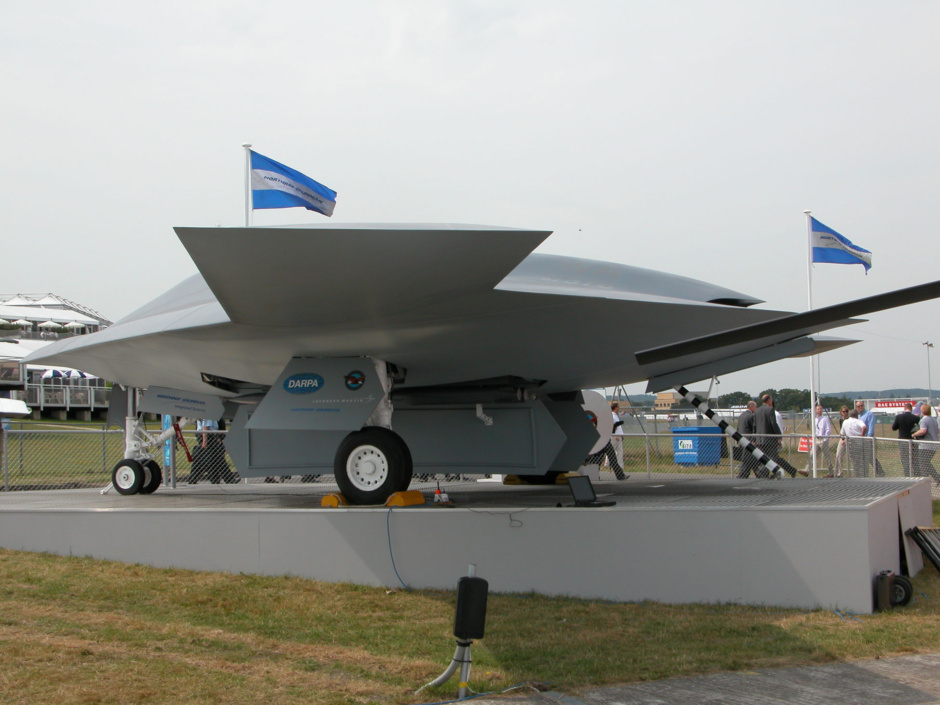
The Navy went on to give Northrop Grumman a contract for a naval UCAV demonstrator with the designation of "X-47A Pegasus", in early 2001. The Pegasus demonstrator looks like a simple black arrowhead with no vertical tailplane. It has a leading edge sweep of 55 degrees and a trailing edge sweep of 35 degrees. The demonstrator has retractable tricycle landing gear, with a one-wheel nose gear and dual-wheel main gear, and has six control surfaces, including two elevons and four "inlaids". The inlaids are small flap structures mounted on the top and bottom of the wing forward of the wingtips.
Pegasus is powered by a single Pratt & Whitney Canada JT15D-5C small high-bypass turbofan engine with 14.2 kN (3,190 lbf) thrust. This engine is currently in use with operational aircraft such as the Aermacchi S-211 trainer. The engine is mounted on the demonstrator's back, with the inlet on top behind the nose. The inlet duct has a serpentine diffuser to prevent radar reflections off the engine fan. However, to keep costs low, the engine exhaust is a simple cylindrical tailpipe, with no provisions for reducing radar or infrared signature.
The UCAV's airframe is built of composite materials, with construction subcontracted out to Burt Rutan's Scaled Composites company, which had the expertise and tooling to do the job cheaply. The airframe basically consists of four main assemblies, split down the middle with two assemblies on top and two on bottom.
The Pegasus was rolled out on 30 July 2001 and performed its first flight on 23 February 2003 at the US Naval Air Warfare Center at China Lake, California. The flight test program did not involve weapons delivery, but Pegasus does have two weapons bays, one on each side of the engine, that may be each loaded with a single 225 kilogram (500 pound) dummy bomb to simulate operational flight loads. The Pegasus was also used to evaluate technologies for carrier deck landings, though the demonstrator did not have an arresting hook. Other issues related to carrier operations involve adding deck tie-downs without compromising stealth characteristics, and designing access panels so that they wouldn't be blown around or damaged by strong winds blowing across the carrier deck.
Specifications (X-47A)
X-47B over sea (CG concept)
This aircraft article is missing some (or all) of its specifications. If you have a source, you can help Wikipedia by adding them.
General characteristics
Crew: none
Length: 19 ft 7 in (8.50 m)
Wingspan: 19 ft 6 in (8.47 m)
Height: 6 ft 1 in (1.86 m)
Wing area: ft² (m²)
Empty weight: 3,836 lb (1,740 kg)
Loaded weight: 4,877 lb (2,212 kg)
Max takeoff weight: 5,903 lb (2,678 kg)
Powerplant: 1× Pratt & Whitney JT15D-5C (X-47A)
Pratt & Whitney F100-220 (X-47B) turbofan, 3,190 lbf (14.2 kN)
Performance
Maximum speed: "high subsonic"
Cruise speed: "high subsonic"
Range: 1,500+ NM (2,778+ km)
Service ceiling 40,000+ ft (12,192+ m)
Rate of climb: ft/min (m/s)
Wing loading: lb/ft² (kg/m²)
Thrust/weight: 0.65
Armament None (ISR)
****************************************
'무기리스트 > 세계우주무기' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 우주정거장 화장실 수리 펌프 디스커버리호에 탑재 (0) | 2008.05.30 |
|---|---|
| 美, 이젠 국방예산 늘려야 (0) | 2008.05.30 |
| 미국 '스텔스 전투기' 괌에 전진배치 (0) | 2008.05.30 |
| 美·中 빠진 ‘집속탄 금지’ 불발탄 ? (0) | 2008.05.29 |
| 화성탐사 로봇 '피닉스' 화성 착륙 성공 (0) | 2008.05.26 |